Understanding Early-Stage Cancer
Early cancer detection may lead to better outcomes.

Why diagnosing cancer early is important
When cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, when it not too big and has not spread, it is more likely to be treated successfully.
That’s why it’s important to keep up with recommended screening tests, attend routine GP check-ups, and see your doctor if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Detecting and treating cancer early may help:

What is Cancer Staging
Cancer staging is a way for doctors to describe the size and location of the cancer (or tumour), whether it has spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes, and if it has spread to other organs. It also helps doctors know how to best treat the cancer and what the outlook or prognosis might be.
To determine the stage, doctors use various tests such as imaging scans, lab tests, biopsies, as well as a physical exam.
Understanding the Stages of Cancer
Most types of cancer are grouped into stages, numbered from 1 to 4, with some starting at Stage 0.
It’s important to note that some cancers use different staging systems, which may have differences in how stages are defined and named.
Everyone’s situation is unique, so if you have cancer, your doctor will explain your cancer stage and what it means for you.
The Stages of Cancer
Stage 1
At this stage, the cancer is small and localised, which means it is limited to the organ it started in.
Stage 2
Cancer at this stage may have grown larger than in Stage 1 but the cancer has not started to spread into nearby tissue. Sometimes the cancer may have spread to lymph nodes near the tumour.
Stage 3
At this stage, the cancer is generally larger and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes and surrounding tissues.
Stage 4
This stage, also known as metastatic or advanced cancer, indicates that the cancer has spread to other organs or other parts of the body.
Early-stage cancer
Early-stage cancer is used to describe cancer that is early in its growth, before it has spread to other parts of the body. Generally, Stage 4 cancers and some Stage 3 cancers are considered more advanced stages and not classified as early-stage cancers.
Pathways following an early-stage cancer diagnosis
In some early-stage cancers, treatment may not be done immediately and instead the doctors will monitor the cancer.
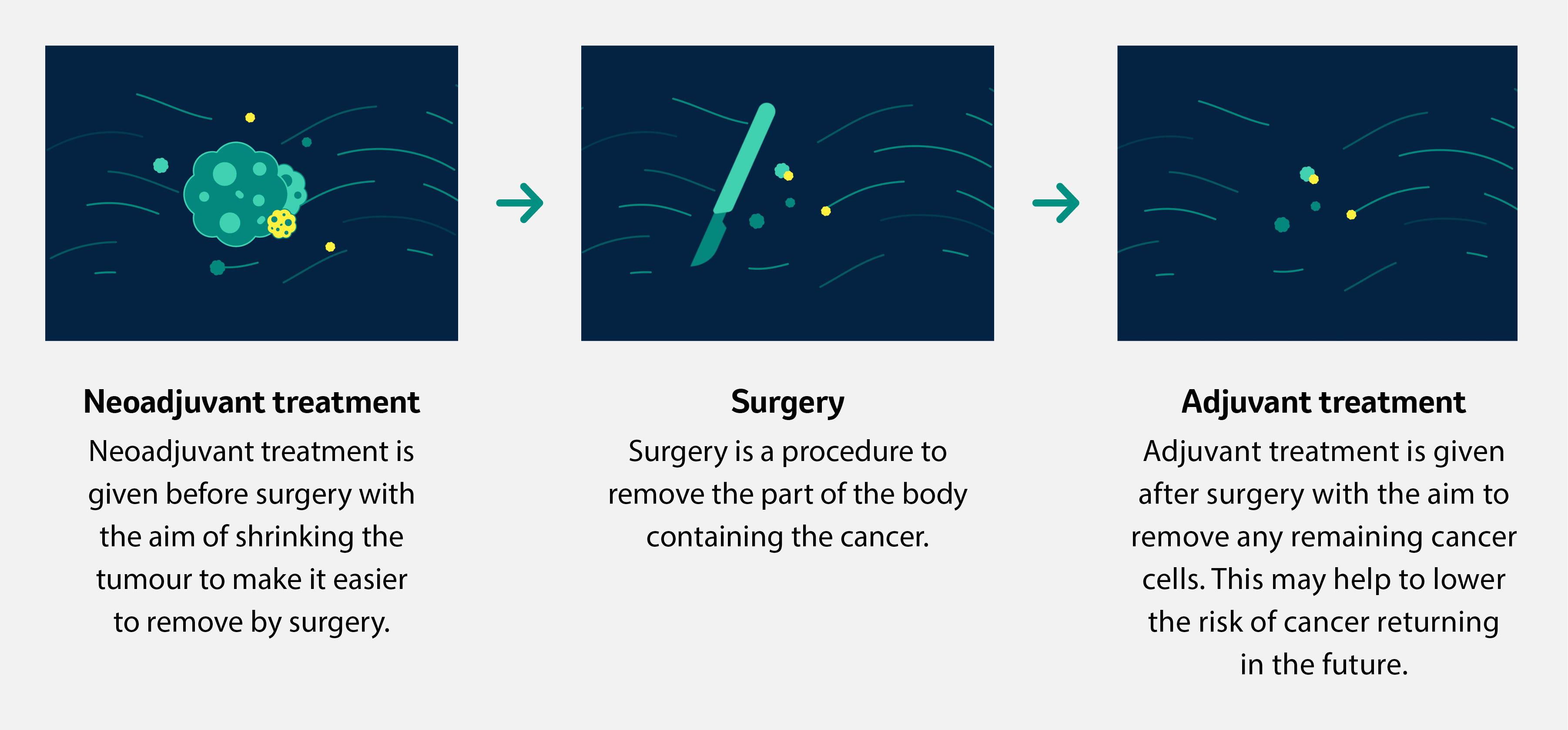
If treatment is recommended, it commonly involves surgery and this may be the only form of treatment that is required. For some types of early-stage cancer other therapies may be used alongside surgery to help shrink the tumour or reduce the risk of cancer returning.
For further information about early-stage cancer please talk to your doctor.
Download our Early-Stage Cancer Care Resource
If you or a loved one is navigating an early-stage cancer diagnosis, this guide is here to help.
The booklet outlines the basics of:
- Understanding the different stages of cancer
- Pathways following an early-stage diagnosis
- Benefits versus risks of early-stage cancer treatment
References:
- Cancer Research UK. Why is Early Cancer Diagnosis Important? Available at: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/spot-cancer-early/why-is-early-diagnosis-important. Accessed on: September 08, 2023.
- Cancer Research UK. Stages of Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/what-is-cancer/stages-of-cancer Accessed on: January 30, 2024.
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Staging. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/diagnosis-staging/staging Accessed on: October 02, 2024.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Staging. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/diagnosis-staging/staging.html Accessed on: October 02, 2024.
- Cancer Society New Zealand. Understanding Lung Cancer. Section 3: Staging Lung Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org.nz/assets/Understanding-Lung-Cancer-booklet-2022-UPDATED.pdf Accessed on: April 04, 2023.
- National Breast Cancer Foundation. Stage 1 or 2 – Early Breast Cancer. Available at: https://nbcf.org.au/about-breast-cancer/diagnosis/stage-1-2-early-breast-cancer/ Accessed on: September 08, 2023.
- Cancer Society of New Zealand. Living Well with Advanced Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancer.org.nz/cancer/types-of-cancer/advanced-cancer/ Accessed on: October 26, 2023.
- Cancer Research UK. Active Surveillance and Watchful Waiting for Prostate Cancer. Available at: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/prostate-cancer/treatment/monitoring-prostate-cancer Accessed on: July 9, 2025.
- Cancer Council Australia. Understanding Surgery: A Guide for People with Cancer, Their Families and Friends, 2023. Available at: https://www.cancer.org.au/assets/pdf/understanding-surgery-booklet Accessed on: September 03, 2023.
- National Cancer Institute. NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Adjuvant Therapy. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/adjuvant-therapy Accessed on: June 26, 2019.
- National Cancer Institute. NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Neoadjuvant Therapy. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/neoadjuvant-therapy Accessed on: October 26, 2023.
TAPS NP23508 TAPS DA 2514KN NZ-NON-00484 V2.0 Last updated October 2025


